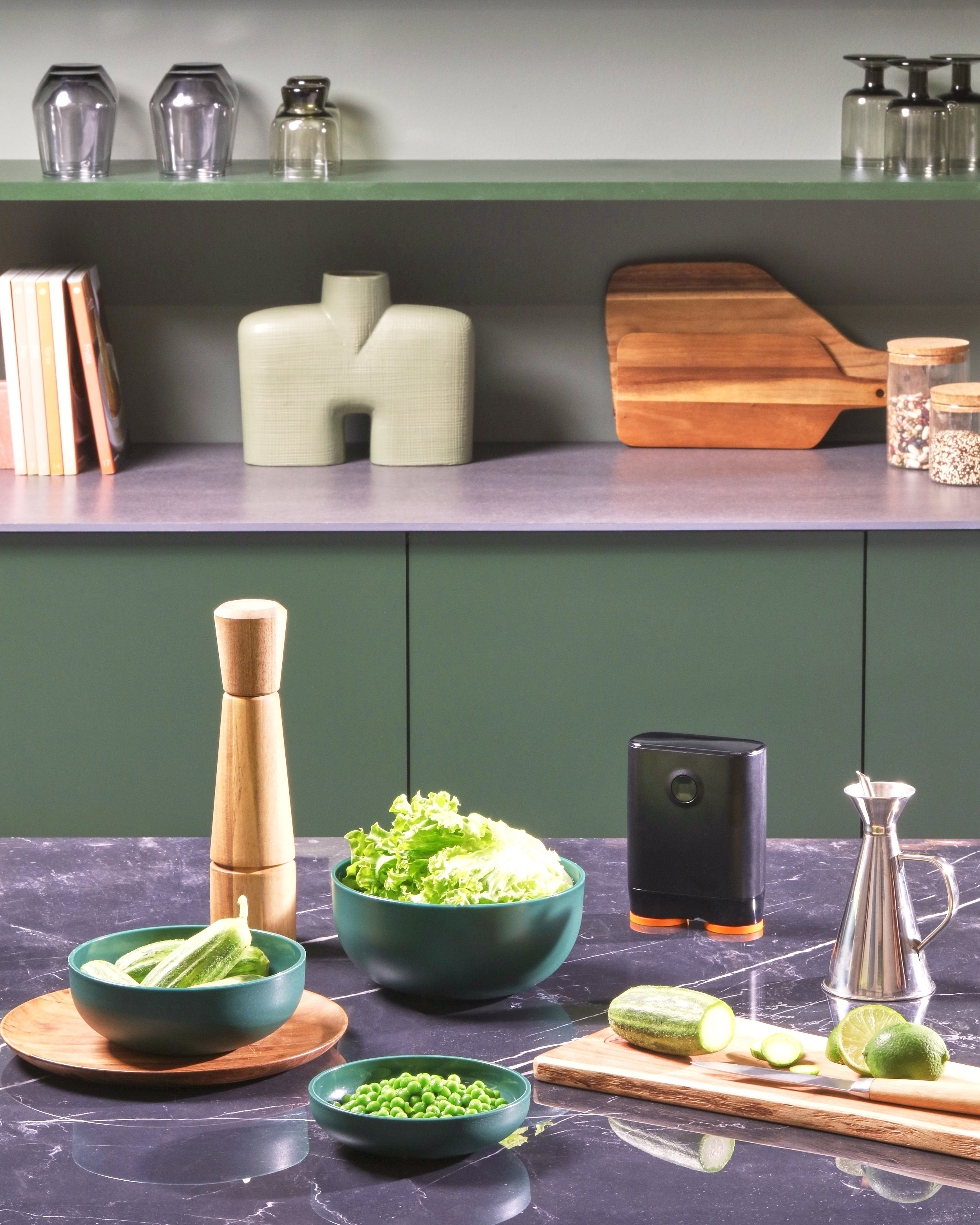
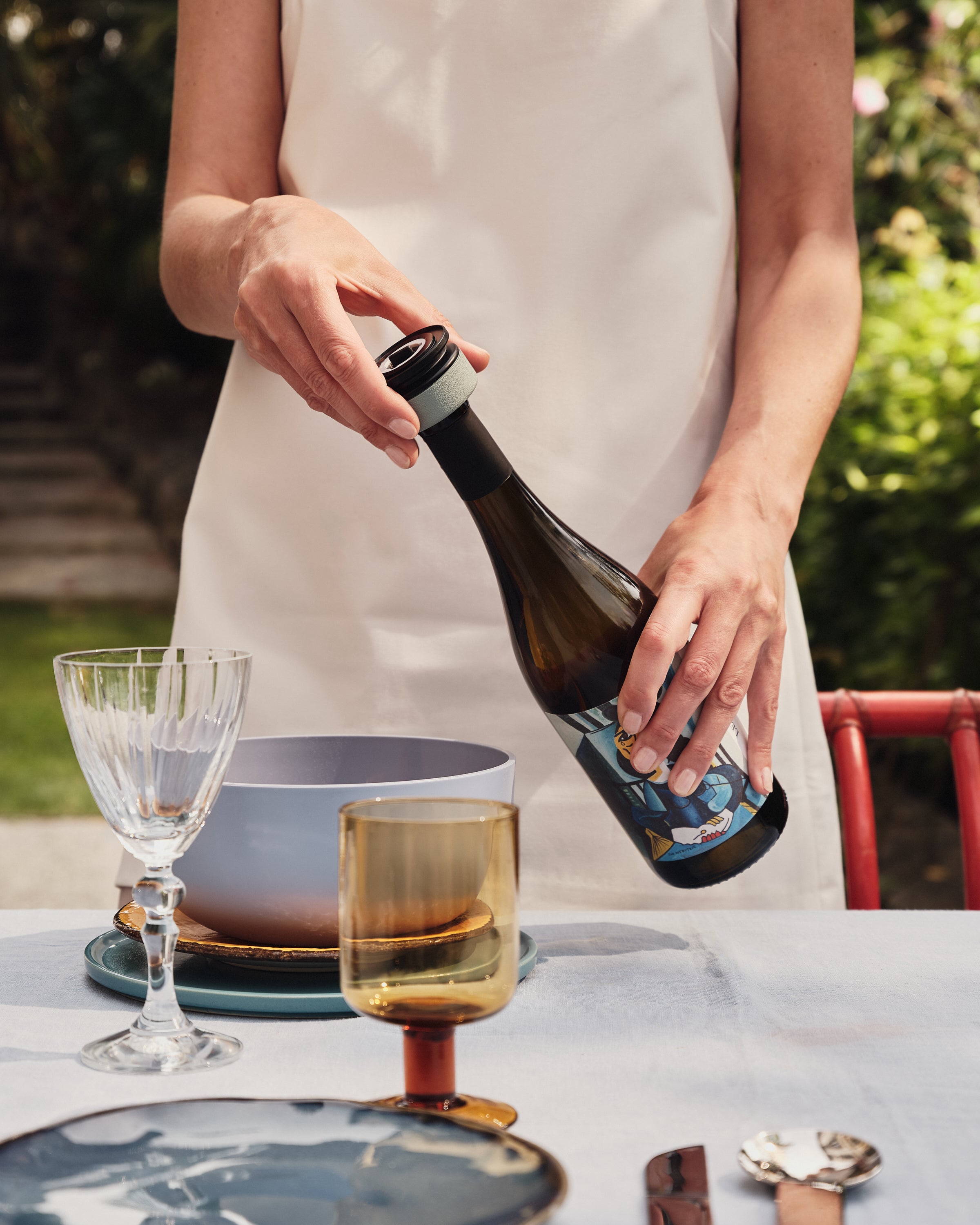
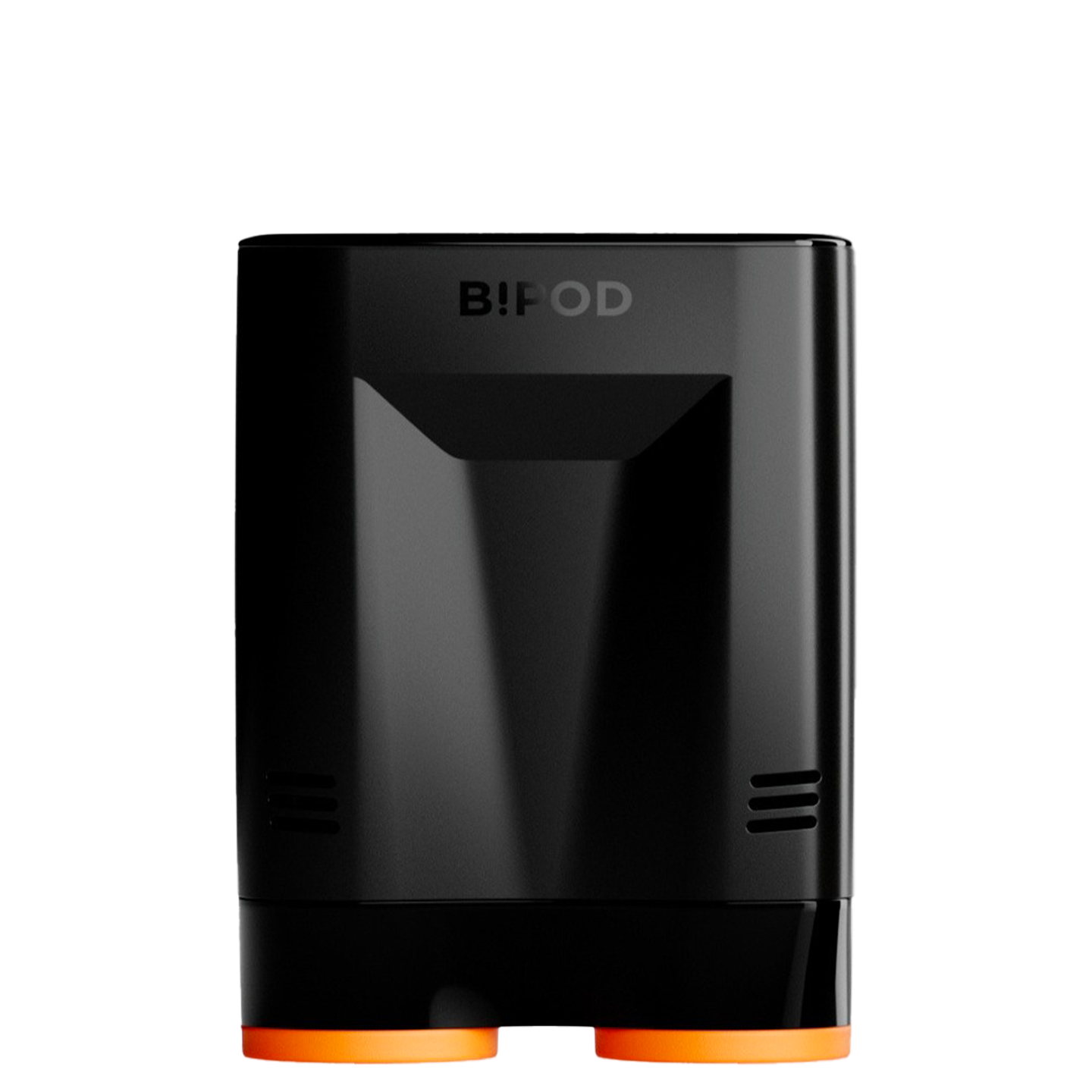
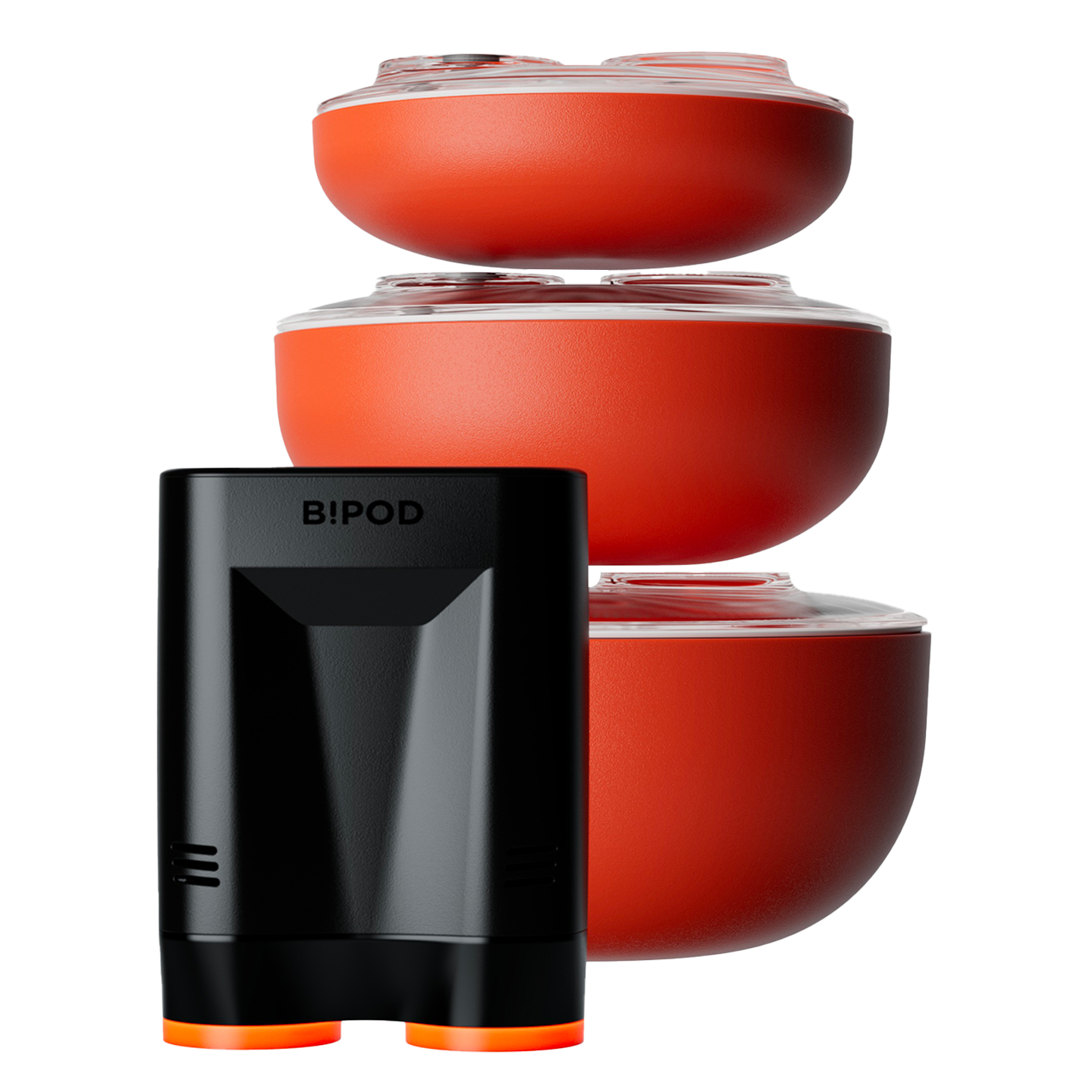
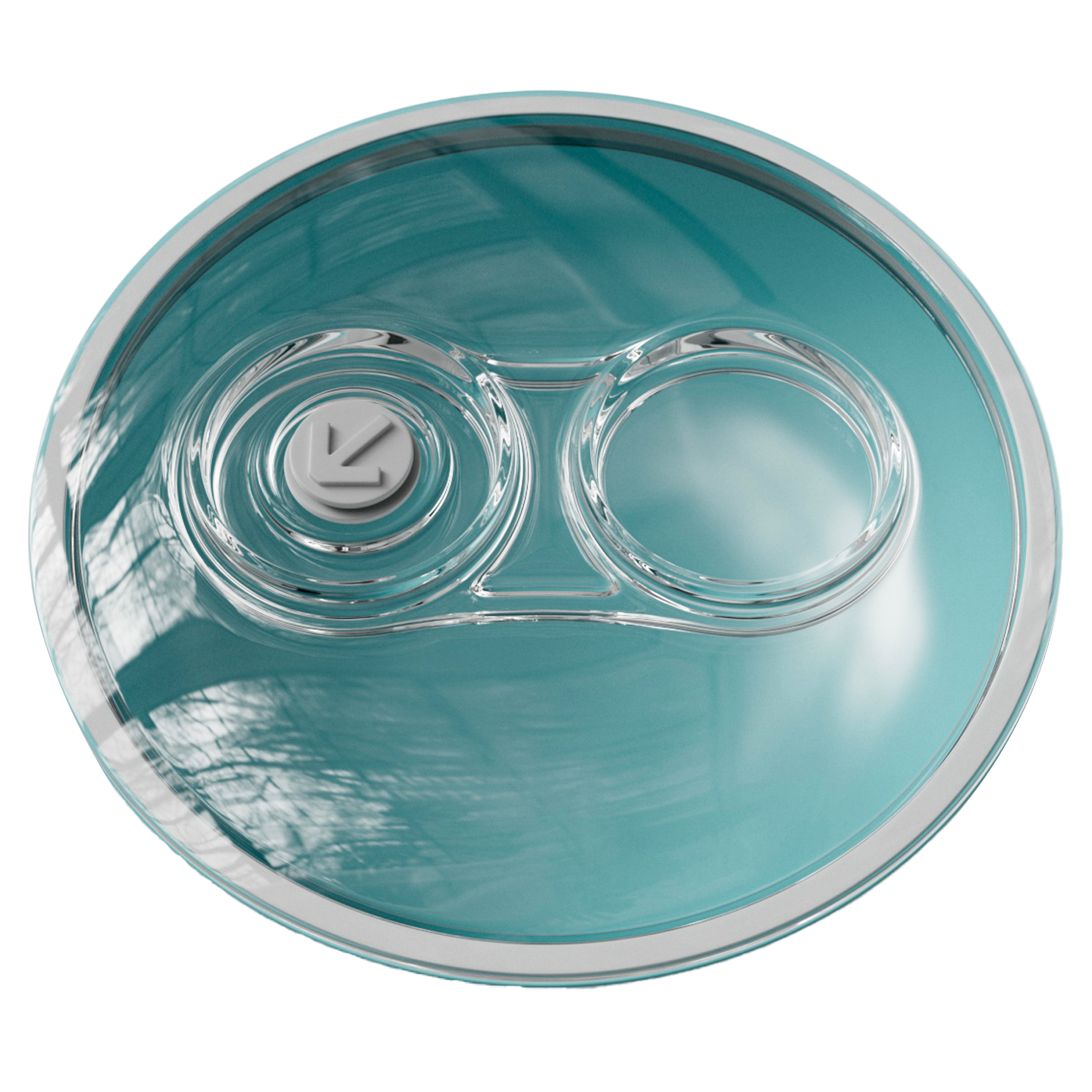
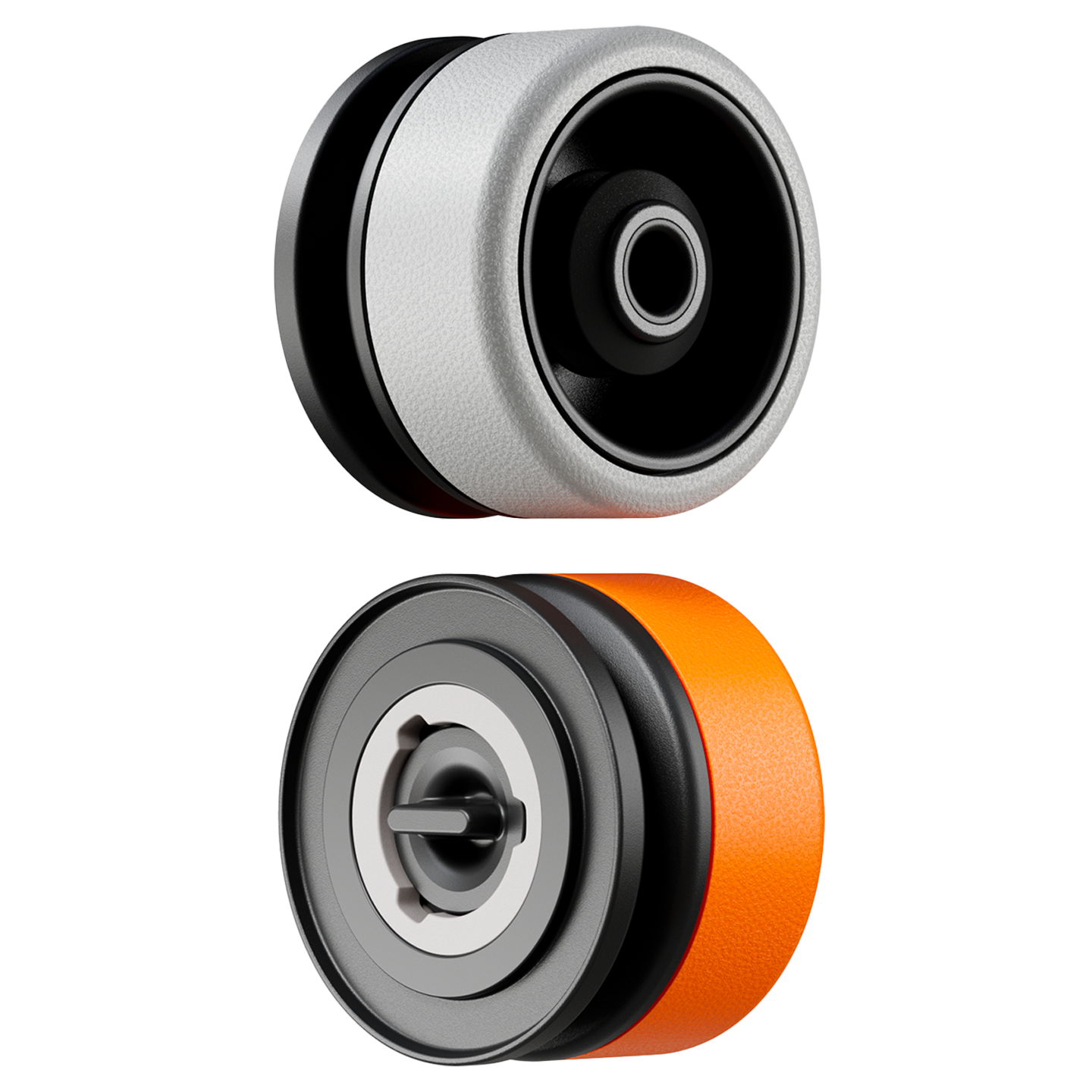
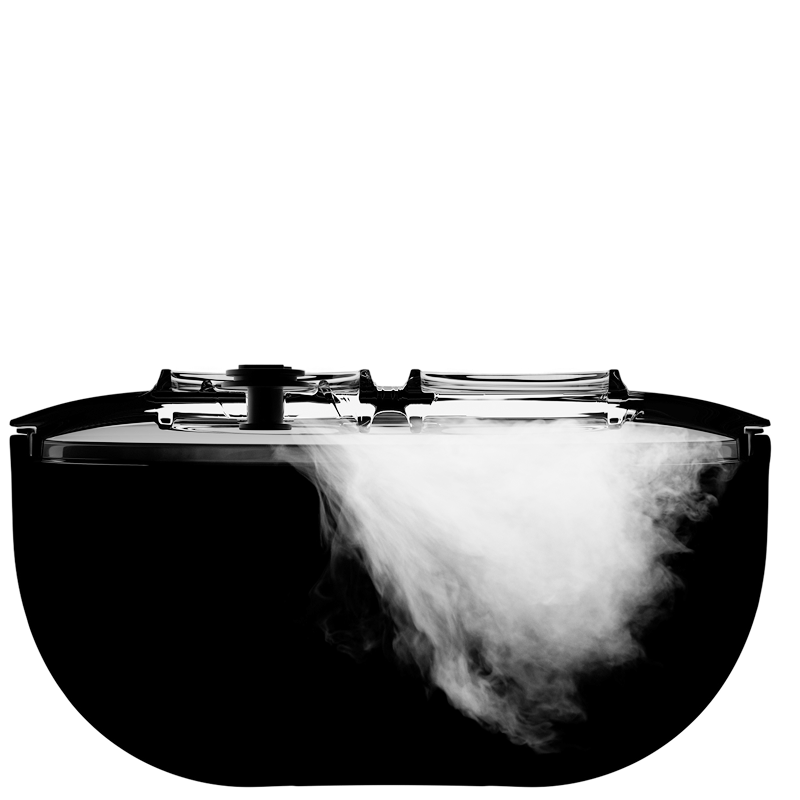
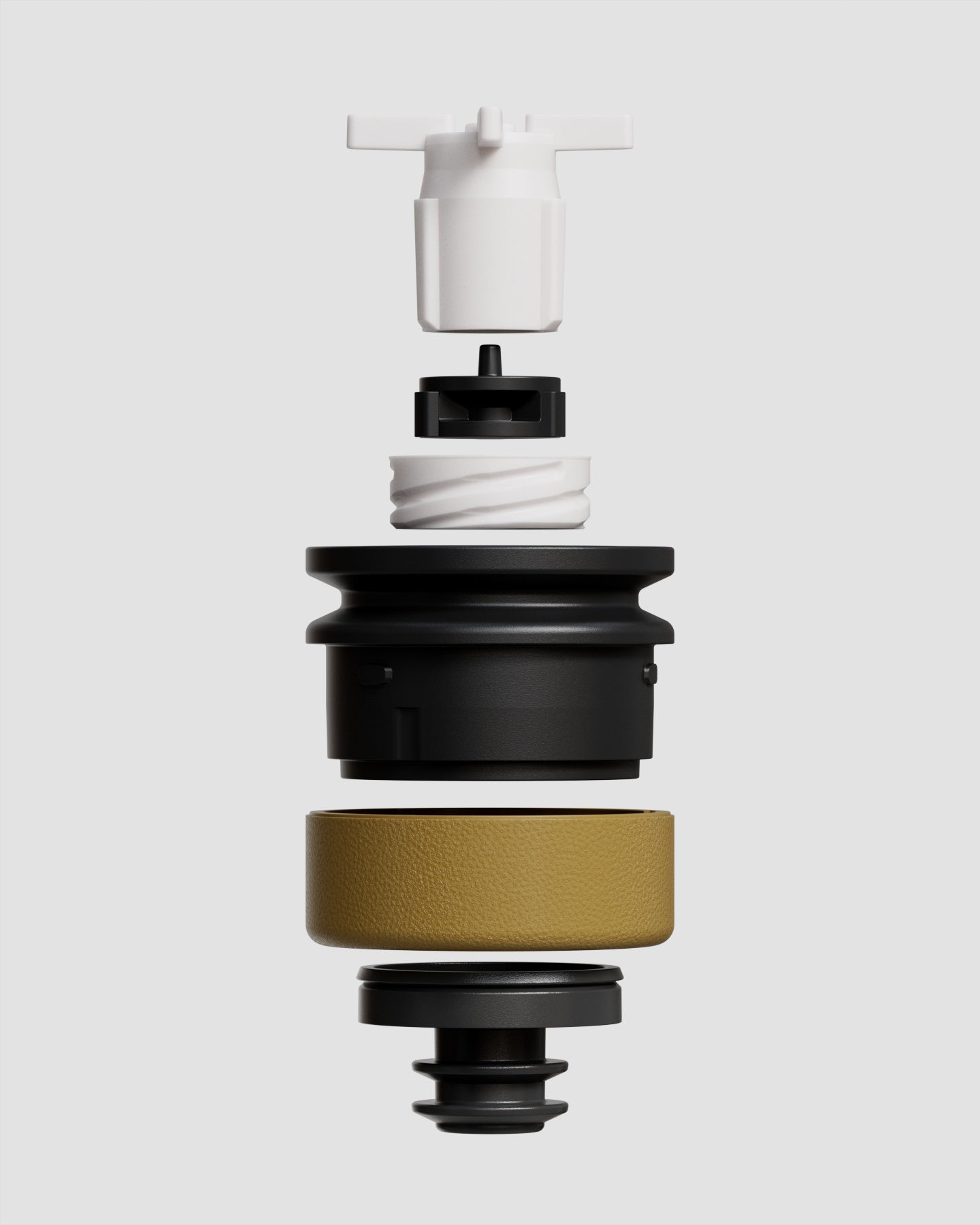
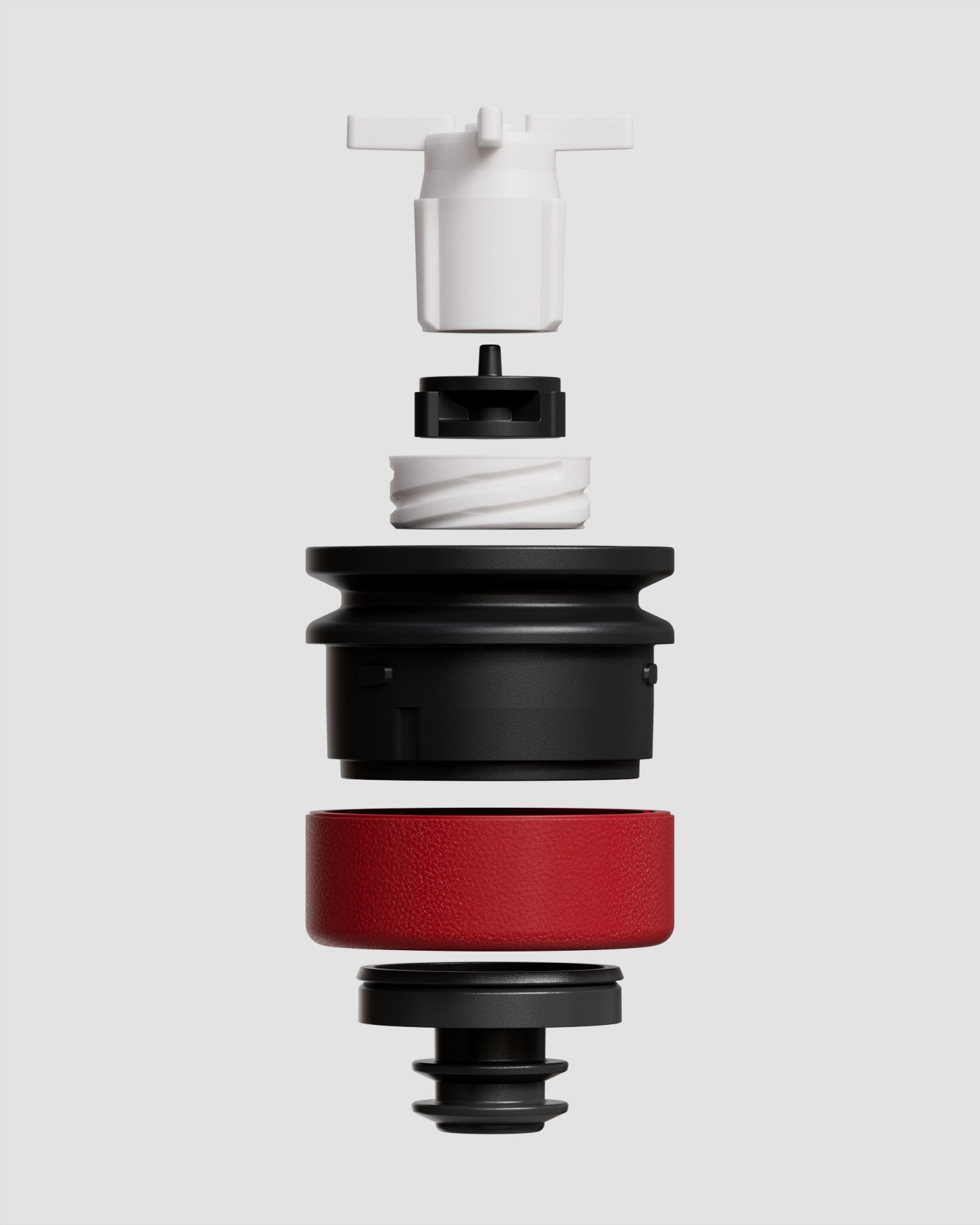
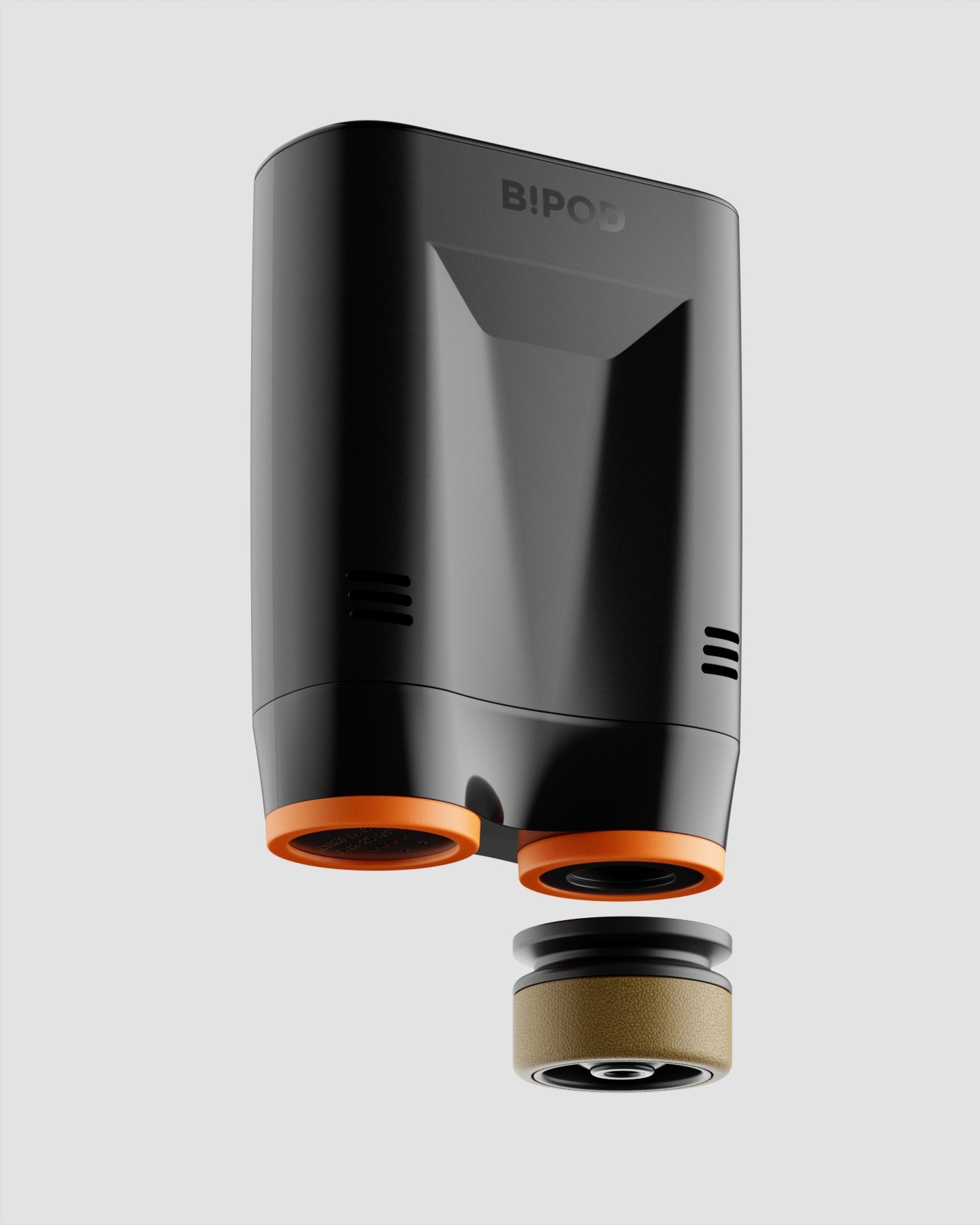
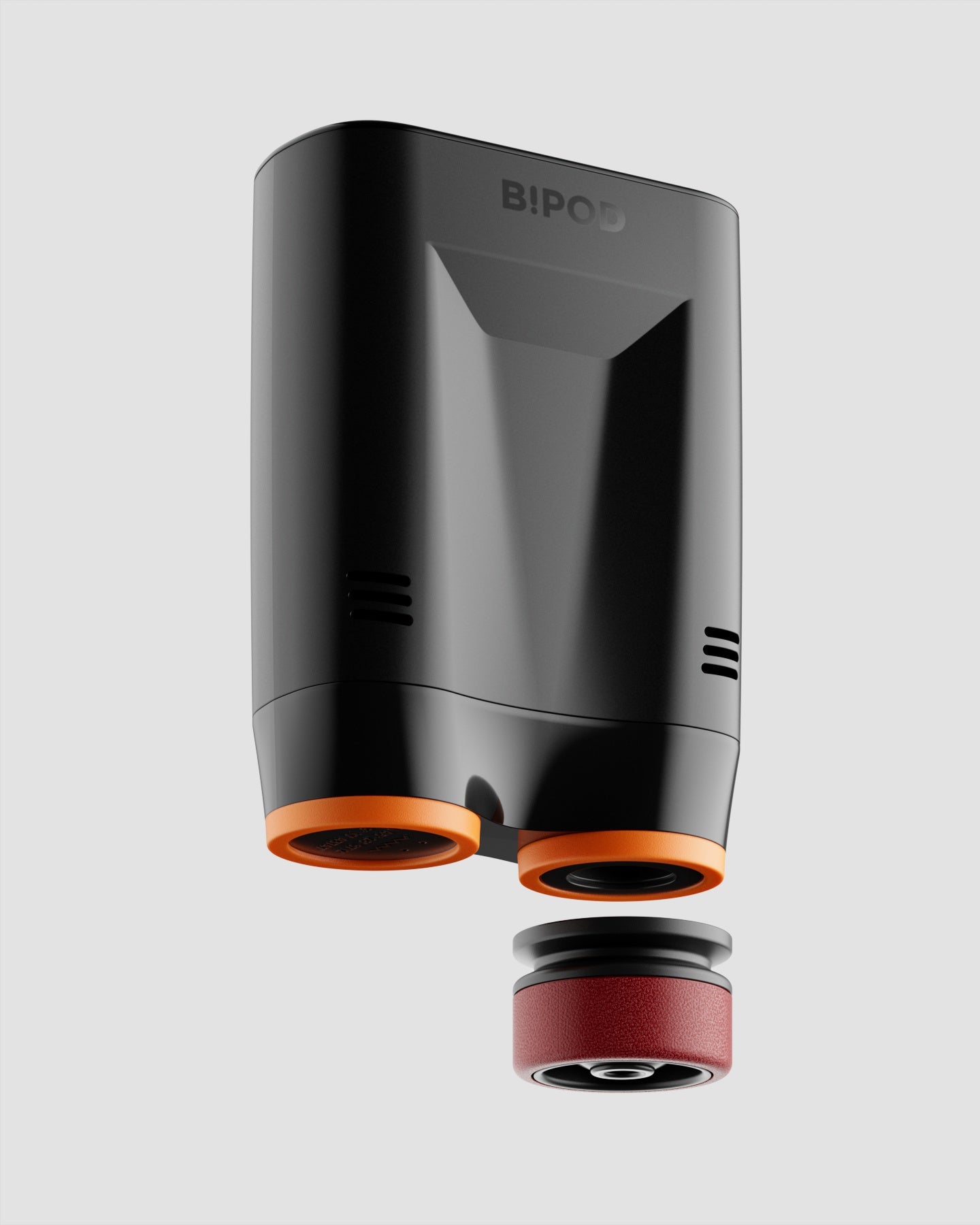
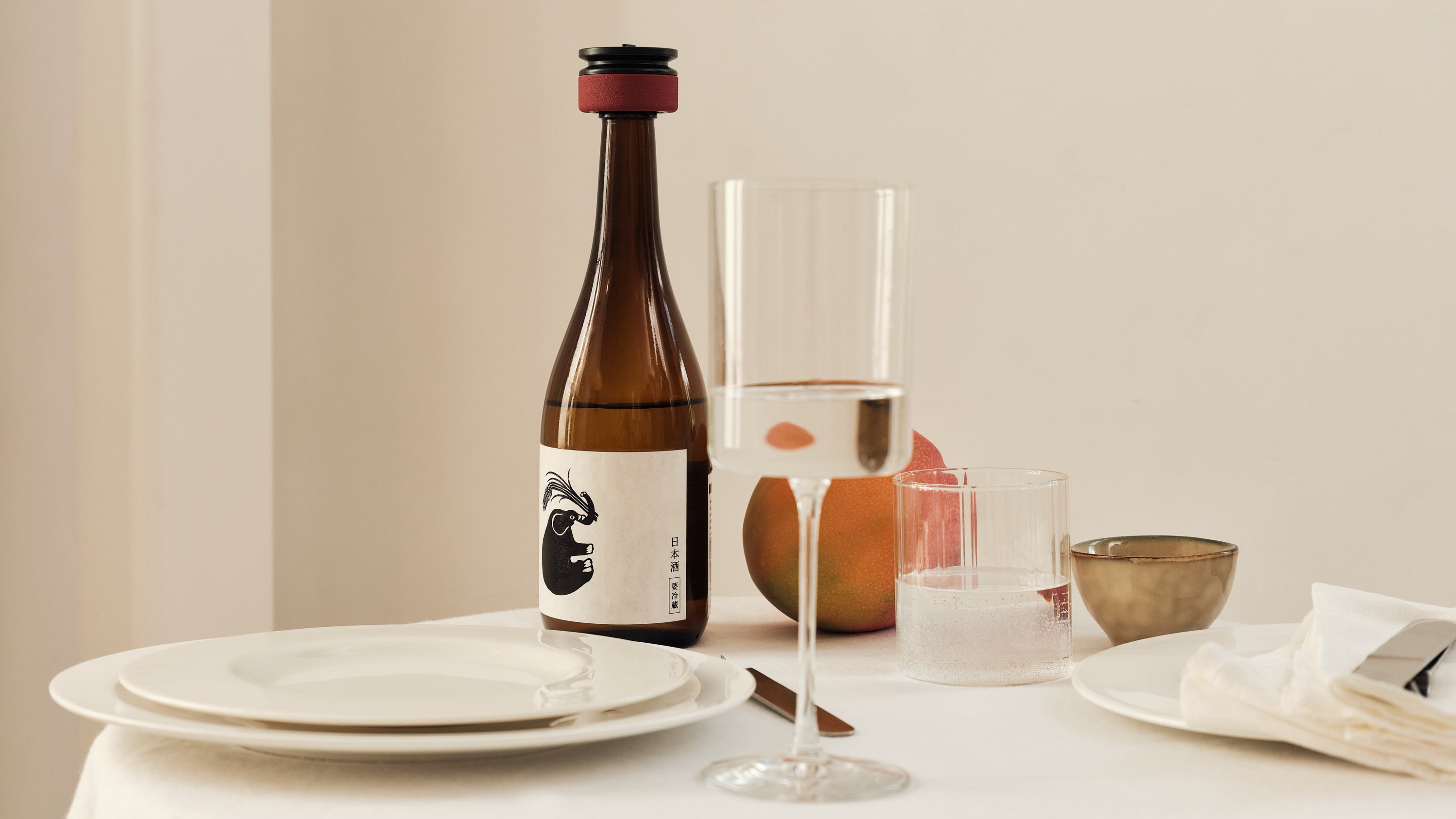
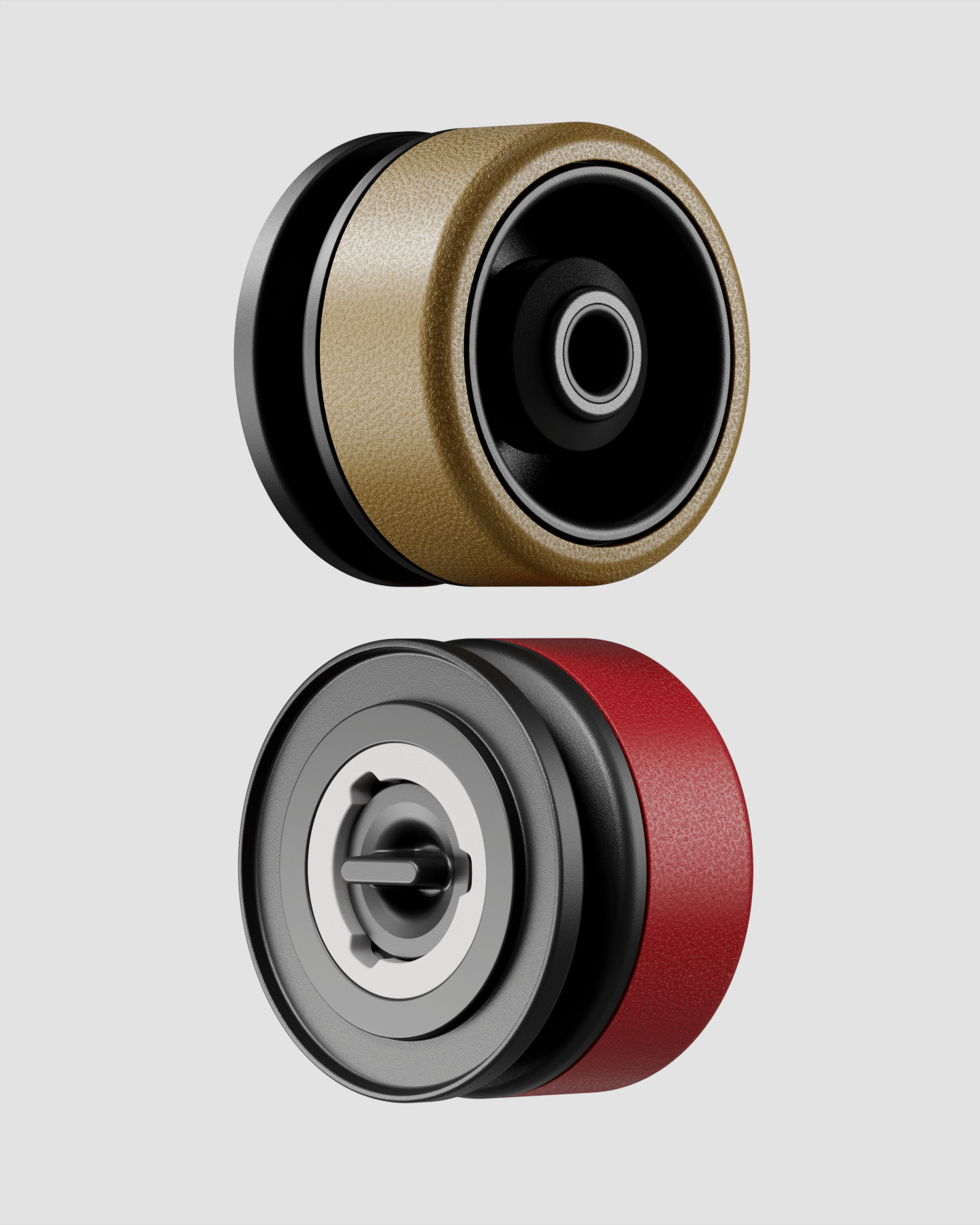
Inspired by samurai helmets, Kabuto is a design-forward vacuum wine saver that protects aroma and flavor by removing oxygen from an opened bottle. Thanks to DRO!D's vacuum technology, it can operate two power modes to adapt to delicate or robust still wines. It comes in a set of two vacuum saver available in three different color combinations.
We're serious about the environment.
This screen helps your monitor use less power when it's inactive or when you step away.